Posts Tagged ‘“Massachusetts concussion law”’
March is Brain Injury Awareness Month
March is Brain Injury Awareness Month. Take the opportunity to learn
Today, there is greater awareness around brain injuries. As a result, many people are treating brain injuries earlier and living healthier lives.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) observes Brain Injury Awareness Month in March, to provide education about potential concussion symptoms, ongoing research and the needs of those living with a brain injury. This comes at the right time for families, as many children and teenagers plan to participate in spring sports.
Many brain injuries are caused by car accidents, falls or violence. But over the past decade, we have learned more about young children and student athletes suffering concussions on the sports field. In fact, from 2010 to 2016, nearly two million children were treated in emergency rooms for sports-related traumatic brain injuries (TBI), according to the CDC website. Sports associated with the highest number of ER visits: football, cycling, basketball, playground activities and soccer.
Among males 17 and younger, football was involved in 27 percent of all sports-related TBI visits to the ER, more than any other activity. In the same age group, females playing soccer, playground activities and basketball made the highest number of ER visits for TBI. Among children under 5, playground activity resulted in the most ER visits for TBI.
As we continue learning about injuries to children and student athletes, research continues to show older Americans are highly vulnerable to brain injuries. They are the most likely to be hospitalized for TBIs, according to the CDC.
At Breakstone, White & Gluck, our attorneys encourage you to look at the CDC website so you can be informed about the symptoms of traumatic brain injury and concussion. If you observe symptoms in yourself or your children, immediately call your doctor to be examined. Also guide older family members to medical treatment. This is paramount because a brain injury left untreated can result in long-term impairment or death. When someone receives immediate treatment, effective diagnosis and management early on is critical.
What is a Traumatic Brain Injury?
According to the CDC, a traumatic brain injury can be caused by a bump, blow or jolt to the head. There are traumatic brain injuries and mild traumatic brain injuries, which are often called concussions.
What are the Symptoms of a Traumatic Brain Injury?
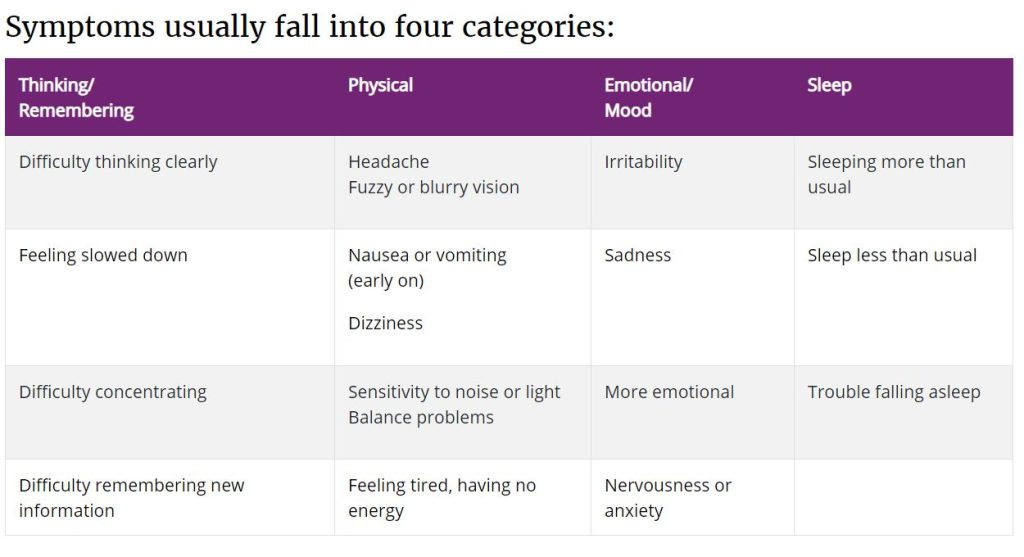
Concussion Symptoms. Courtesy CDC Website
You may observe some of these symptoms immediately after someone sustains a brain injury. Or symptoms may not emerge for several days. It’s also important to note that not everyone experiences the same symptoms.
Symptoms include difficulty thinking, concentrating or remembering or feeling slowed down.
Physical symptoms may include headaches, nausea, vomiting or fatigue. Some people are sensitive to noise or light. Others have trouble balancing themselves.
When someone suffers a head injury, it’s common for their sleep to be disrupted. They may sleep more or less than normal. Another sign is having trouble falling asleep. More extreme emotions are another symptom. The person may be irritable, sad, more emotional or exhibit high anxiety and nervousness.
Younger children may exhibit some of the above symptoms, but parents should also watch for crying inconsolably, more temper tantrums or getting easily upset and having trouble keeping up with skills they are learning (toilet training for instance). They may also lack interest in their normal activities.
Sports-Related Concussions and TBI in Massachusetts
Be aware of how concussions happen. After a car accident or truck accident, always receive immediate medical attention to make sure you have not suffered a TBI. When an elderly relative slips or a child falls on the playground, check in with the doctor. Do this anytime you observe someone suffer from any type of physical impact to the head.
When you sign your child up to play a sport, ask the coaches for the concussion protocol. In Massachusetts, middle and high schools are required to have documented procedures regarding concussion injuries and prevention. Passed in 2010, M.G.L. c.111 § 222 requires parents and students to participate in concussion awareness training so they can recognize symptoms and receive early treatment. The law also requires students to be removed from play if they may have suffered a concussion. They can only return with medical clearance.
Under the law, public middle and high schools and those subject to Massachusetts Interscholastic Athletic Association (MIAA) regulations must have concussion protocols. Other sports leagues are not required under Massachusetts law, but they should all have a concussion policy on their website.
Final Note
- At home, educate older children about TBI symptoms. Ask them questions when you sense something may be off and use the above chart to determine whether you may need to call the doctor.
- Ask for concussion safety protocols at schools and daycare centers, and when children participate in sports leagues. Attend concussion trainings.
- Watch younger children and older adults closely. Remember young children may not be able to communicate symptoms and pain with you and older adults may not recognize symptoms in themselves, especially if they have other medical conditions.
- Recruit as many family members as you can in watching for signs in young children, teens and the elderly.
- Visit some of the online resources below and share them with family members.
Concussion Prevention Resources for Families
Massachusetts Law on Concussion Prevention in Sports
105 CMR 201.00: Head injuries and concussions in extracurricular activities
Additional Resources
Heads Up to Brain Injury Awareness Training, CDC
Facts About Concussion and Brain Injury – Where to Get Help, CDC (a resource for all ages)
Sports Related Concussions and Head Injuries, Mass.gov
Concussion Trainings, Massachusetts Department of Public Health
Returning to School After a Concussion, Mass.gov
About Breakstone, White & Gluck – Boston Personal Injury Lawyers
With more than 100 years combined experience, Breakstone, White & Gluck of Boston is one of the most respected personal injury law firms in Massachusetts. Our attorneys represent individuals who have suffered traumatic brain injuries or mild traumatic brain injuries due to the negligence of another individual, organization or corporate entity.
If you have been injured, learn your legal rights for seeking financial compensation and obtaining medical care. For a free legal consultation, call Breakstone, White & Gluck at 800-379-1244 or 617-723-7676 or you can use our contact form.
Massachusetts Concussion Legislation Would Ban Students In Grade 7 or Younger from Playing Football
Should students have to wait until they finish 7th grade to play football in Massachusetts? Lawmakers are being asked to consider legislation to delay the start of play to protect players from concussions.
“An Act for No Organized Head Impacts to Schoolchildren,” has been filed by State representatives Paul A. Schmid III (D-8th Bristol) and Bradley H. Jones Jr. (R-20th Middlesex). The legislation would ban children in 7th grade or younger from playing or practicing any form of organized tackle football. Schools would be held accountable and face fines for violations:
- $2,000 for each violation
- $5,000 for subsequent violations
- $10,000 when serious physical harm result to participants
Children would be allowed to play flag football or any form of football which does not involve tackle play. The proposal does not include any other sport.
Causes of Concussions
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) define a traumatic brain injury (TBI) as a disruption to the brain caused by a blow or jolt to the head. Concussions are considered a mild TBI, which can result in a brief change of mental alertness or consciousness. A severe TBI can result in a longer period of unconsciousness or mental change.
Symptoms may not be immediately evident after a concussion, especially if the person or those around them are not familiar with the symptoms, which can include an inability to think clearly, memory problems, feeling dazed and mood, behavior or personality changes. Headaches, nausea and vomiting can also set in.
Beyond the sports field, falls are the leading cause of concussions, according to the CDC. Adults over age 65 and children under 14 are most likely to suffer a fall leading to a head injury. Car crashes are the third leading cause of concussions, followed by being struck in the head by an unspecified object, such as in a construction site accident or by violence.
Concussions can also happen on the sports field. Not every contact necessarily results in a concussion, but to identify injuries, Massachusetts and other states have already passed concussion education and training laws. Known as “return to play” laws, these require high school and middle school students to be examined by a medical professional before they can participate in sports again.
Research on Concussions and the Impact on Younger Football Players
New research shows there is a measurable impact when younger children play football. In a study of 26 football players – all age 12 – Wake Forest researchers found changes in the corpus callosum, which joins the two sides of the brain and integrates cognitive, motor and sensory functions. The players underwent MRIs to examine the changes prior to the three-month season and three months after the season concluded. They were compared to 22 other students who did not participate in contact sports.
Players who suffer a concussion need proper rest and treatment so they can properly heal and to reduce the chance for another injury. Researchers have documented this risk; one study found high school and college students who sustained concussions were four to six times more likely to suffer a second injury (Source: McGill University in Montreal).
Concussion Legislation Filed in Other States
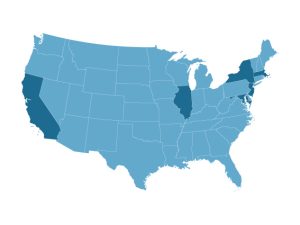
Lawmakers in Massachusetts and five other states have proposed banning tackle football for children younger than 12 or for those in seventh grade or younger. Data from Shape America.
Massachusetts isn’t taking the field alone on concussions. At least five other states are also debating tackle football bans for children under age 12. These states include Illinois, California, Maryland, New York and New Jersey, according to Boston.com. But none of the proposals are on track to reach state governors.
All 50 states already have “return to play” laws aimed at reducing youth sports-related concussions, according to the National Conference of State Legislatures. Washington state was the first to pass such a law in 2009. By 2015, every other state had enacted a similar law.
In most states, these laws mandate concussion awareness training and education to prevent concussions among student athletes. According to Shape America, 48 states require students suspected of having concussions to sit out at least 24 hours.
Arizona and South Carolina allow students back on the field the same day with a doctor’s approval.
Passed in July 2010, the Massachusetts concussion law requires parents, volunteers, coaches and school nurses to receive specialized concussion awareness training. This is to help them recognize concussion symptoms and help students receive treatment as soon as possible.
As in other states, the Massachusetts law requires medical clearance before students can return to sports. Schools are then required to maintain detailed record-keeping related to a student’s injury and progress in the classroom and on the field. The law is M.G.L. ch.111 §222. The Code of Massachusetts Regulations is 105 CMR 201.000.
All middle and high schools which offer sports through the Massachusetts Interscholastic Athletic Association (MIAA) must follow the concussion safety law.
Head Injuries and Concussions Being Tracked Among Massachusetts Student Athletes
 More than 330 students suffered head injuries and concussions last fall at 26 high schools in the region, according to a survey by The Boston Globe. This is the first time Massachusetts high schools and middle schools have been required to report injuries under a new state law.
More than 330 students suffered head injuries and concussions last fall at 26 high schools in the region, according to a survey by The Boston Globe. This is the first time Massachusetts high schools and middle schools have been required to report injuries under a new state law.
Football accounted for the majority of injuries, with 207 reported head injuries. Girls soccer followed with 85 head injuries, compared with 46 among boy soccer players.
Robert Cantu, a clinical professor of neurosurgery at Boston University School of Medicine, told theGlobe that football is the leading cause of head injuries among student high school athletes nationwide. He estimated that for every concussion recognized in football, 6 to 8 go unreported.
Concussions are a brain injury which can result when student athletes are struck in the head, collide with each other or engage in unsafe play. One recent study has documented how excessively heading the ball in soccer causes trauma to the brain as well. Symptoms can include headache, nausea, dizziness and confusion. Concussions have the best chance for recovery when given proper rest.
In 2010, Massachusetts passed a new law aimed at preventing concussions among high school athletes and protecting them from long-term injury. Since last September, students, parents and coaches have been required to receive annual training on recognizing and treating concussions; students who sustain concussions must obtain medical clearance before returning to play. Schools must report the number of injuries to the state Department of Public Health.
The 26 schools reported 338 head injuries. Marshfield and Newton South high schools reported the largest number of head injuries, followed by Lexington, Duxbury and Wakefield. Some coaches in these districts say the higher numbers reflect the community’s work to educate students and parents.
Some schools have gone beyond the requirements of the law and are utilizing ImPACT testing, a computerized cognitive test used to help evaluate whether a student is ready to return to the field. Some school districts are providing free physicals and staffing a doctor at every football game.
Finally, some athletic directors report their coaches are focusing on safe playing techniques while others are seeking new football helmets for players.
Related:
- Massachusetts Concussion Law
- Massachusetts Baseball Safety
- Massachusetts Interscholastic Athletic Association